Why Google Isn't Indexing Your AI Content And How To Fix It
Google isn't indexing your AI content due to GSC permission errors, IndexNow verification issues, or content quality flags. Verify API keys, check status codes, and monitor submission logs.
Google won't index your AI content when permissions are missing, IndexNow verification fails, or quality signals don't meet baseline standards.
Most indexing failures trace back to Google Search Console access errors, API key mismatches, or content that triggers spam filters. The fix starts with verifying your GSC property ownership and checking IndexNow key files are hosted correctly at your domain root.
You've published 50 AI-generated blog posts this month. Your content calendar is full. Your workflow feels automated and efficient. But when you check Google Search Console three weeks later, only 4 pages are indexed.
This scenario plays out constantly for teams using AI content automation. The publishing part works perfectly. The indexing part? That's where things break down. Let's walk through exactly why Google isn't picking up your AI content and what you need to fix right now.
Common GSC Permission and Verification Errors
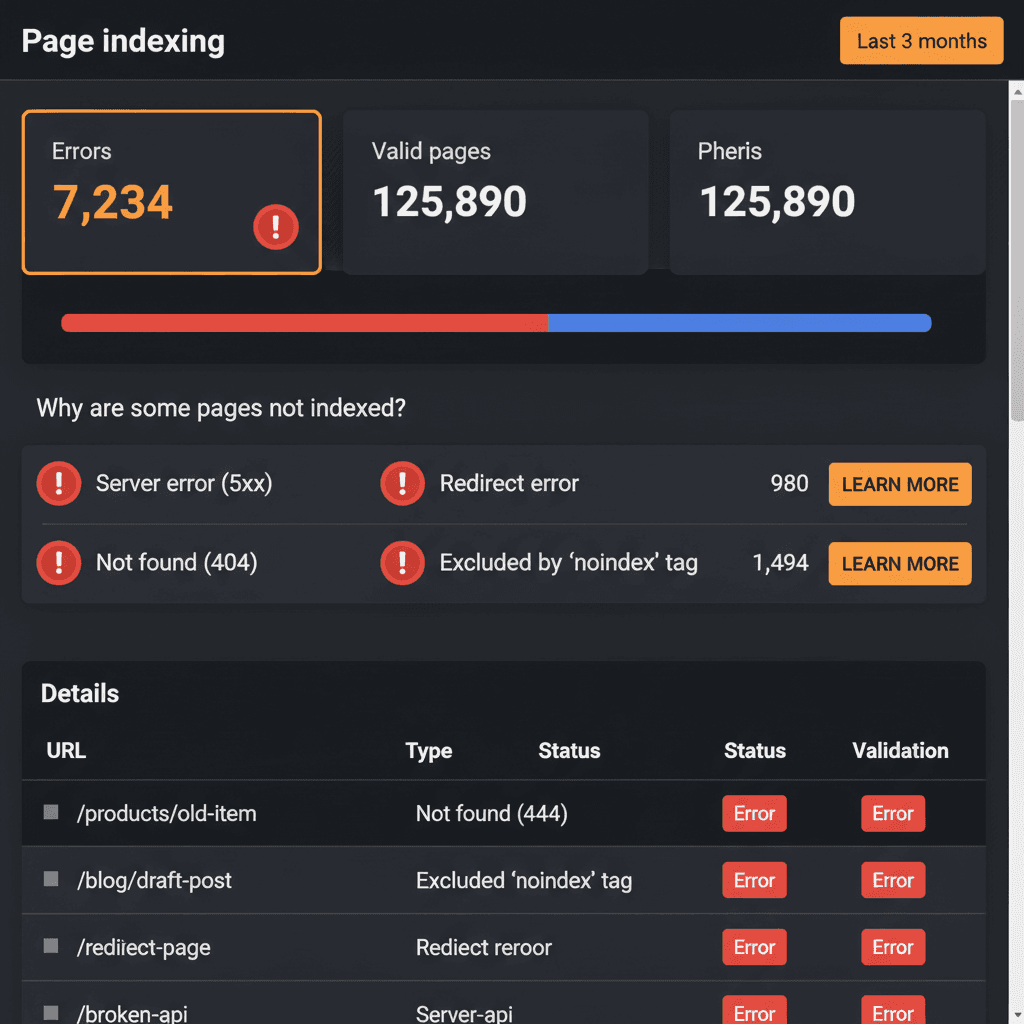
Before Google can index anything, it needs to verify you own the domain and have permission to submit URLs. We're seeing three recurring permission issues in 2024.
Is the recent Google update silently cutting off your content? Check if your page exceeds 2MB now.
Missing or Expired GSC Property Access
Your Keytomic account connects to Google Search Console through OAuth or domain verification tokens. If that connection expires or was never set up properly, your auto-indexing submissions go nowhere.
Check your GSC property list. Navigate to Settings → Users and permissions. Verify the service account or OAuth token Keytomic uses appears in the verified users list with "Owner" or "Full" permissions. If it's missing, you'll need to re-authenticate.
According to Google's Page Indexing documentation, "the server encountered a 4xx error" often means authentication failed during the indexing request.
Domain Verification Token Conflicts
You added a meta tag to verify ownership in GSC. Then your CMS updated and stripped it out. Or you switched from DNS verification to HTML file upload and left the old method active, creating conflicts.
GSC allows multiple verification methods, but mixing them incorrectly can cause intermittent failures. Pick one method and stick with it. DNS TXT records are most reliable for automated workflows because they don't depend on page-level changes.
Robots.txt Blocking Googlebot
This one's embarrassing but common. Your staging site had Disallow: / in robots.txt. Someone migrated that file to production. Now Google can't crawl anything, even though you're submitting URLs through the API.
Verify your robots.txt file at yourdomain.com/robots.txt. Look for any Disallow directives that might block Googlebot. A properly configured file for auto-indexing should look like:
IndexNow API Setup and Verification Steps
IndexNow is the instant submission protocol that notifies Bing, Yandex, and participating search engines when you publish or update content. Setting it up incorrectly is the number one reason auto-indexing fails.
Generating and Hosting Your API Key
You need a unique API key to prove domain ownership. Visit Bing's IndexNow key generator and create a 32-character hexadecimal key.
Download the key file. It will be named something like 7ae1f6c10bc648c1bf556d1e51496722.txt. Upload this file to the root directory of your website. The file must be accessible at:
https://yourdomain.com/7ae1f6c10bc648c1bf556d1e51496722.txt
The file content should contain only the key itself. No extra characters, no formatting, just the key string.
Common Key File Hosting Mistakes
We've seen teams upload the key file to /public/ or /assets/ instead of the root. IndexNow looks for it at the domain root only.
Another issue: incorrect file encoding. The key file must be UTF-8 encoded plain text. Opening and saving it in certain text editors can add invisible BOM characters that break verification.
Test your key file manually. Visit the URL in your browser. You should see only the key string displayed as plain text.
Verifying API Key Submission Format

When your automation platform submits URLs to IndexNow, it needs to include the key location parameter. The request format looks like:
If the keyLocation parameter points to the wrong file path or the key string doesn't match what's in the file, IndexNow returns a 403 error and rejects your submission.
Checking IndexNow Submission Status
After submitting URLs via IndexNow, you can verify receipt in Bing Webmaster Tools. Navigate to Reports & Data → IndexNow to see submission status and timestamps.
A 200 response code means the submission was accepted. It doesn't guarantee indexing, but it confirms the request went through. A 400 or 403 response means verification failed.
If you're getting consistent 403 errors, regenerate your API key and upload the new file. Wait 24-48 hours before deleting the old key file so search engines have time to update their records.
Crawled Currently Not Indexed and Other Common Error Codes
Google's Page Indexing report groups errors into specific categories. Understanding what each error means tells you exactly where to look for fixes.
Server Error (5xx)
Your server returned a 500-level error when Googlebot requested the page. This could be a temporary overload, a misconfigured server, or excessive page load times.
Check your server logs for 500, 502, or 503 errors around the time Google attempted to crawl. If you're seeing spikes during Googlebot visits, you might need to increase server resources or implement caching.
Google's indexing documentation notes that "dynamic page requests can cause excessive load times."
Submitted URL Marked 'noindex'
You submitted the URL for indexing via sitemap or API, but the page includes a noindex meta tag or HTTP header. Google found the page but was instructed not to index it.
Inspect the page source. Look for:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
Or check HTTP headers for:
X-Robots-Tag: noindex
Sometimes these tags are added by SEO plugins set to prevent indexing during development. Other times, they're dynamically generated based on page type or category settings.
Crawled — Currently Not Indexed
This is the most frustrating error. Googlebot crawled your page without issues but decided not to add it to the index "for the time being."
According to SEO Testing's analysis, this usually means Google doesn't see enough value or uniqueness to justify indexing. The page isn't technically broken, but it doesn't meet quality thresholds.
For AI content, this often signals that Google detected patterns associated with low-quality automated output: repetitive phrasing, lack of original data, thin content with minimal depth.
Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
Google found multiple versions of the same content and you didn't specify which version is canonical. Common causes include URL parameters, HTTP vs HTTPS variants, or www vs non-www versions.
Check your canonical tags. Every page should include:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.yourdomain.com/preferred-url" />
Make sure the canonical URL points to the version you want indexed.
Redirect Error
The page has a redirect chain longer than one step, or the final destination returns a 404. Google encountered the redirect but couldn't resolve it to a valid page.
Use a redirect checker tool to trace the full chain. Ideally, redirects should be one-step: Page A → Page B (final destination). Anything longer slows down crawling and risks indexing failures.
Soft 404
Your page returns a 200 status code but displays content that looks like a 404 error page. Google sees the 200 code but recognizes the page has no value, so it doesn't index it.
This happens when custom 404 pages are misconfigured to return 200 instead of 404 status codes. Fix your server configuration to return proper HTTP status codes.
How to Verify Successful Indexing Using GSC and Logs
Submitting URLs is only half the battle. You need to confirm Google actually indexed them and track any failures.
Using the URL Inspection Tool
Google Search Console's URL Inspection Tool shows you exactly how Google sees a specific page. Enter any URL from your site to see:
Current indexing status
Last crawl date
Crawl errors encountered
Whether the page is in Google's index
If a page shows "URL is not on Google" but you submitted it weeks ago, click "Test live URL" to trigger a fresh crawl. Google will fetch the page in real-time and report any issues.
The live test often reveals problems like JavaScript rendering failures, blocked resources, or content that only appears to logged-in users.
Checking Index Coverage Reports
Navigate to Index → Pages in GSC. You'll see a chart showing indexed pages vs excluded pages over time. Below that, you'll find detailed breakdowns of why pages were excluded.
Click into each error category to see the affected URLs. Sort by "Last crawled" to identify patterns. If all your recent AI content submissions show "Crawled — currently not indexed," that's a content quality signal, not a technical problem.
Monitoring Sitemap Submission Status
If you're submitting URLs via XML sitemaps, check the Sitemaps report in GSC. It shows how many URLs you submitted vs how many Google indexed.
A low indexing ratio (submitted 500, indexed 50) indicates either duplicate content issues, quality problems, or crawl budget limitations. For large sites, split sitemaps by content type or publication date to get more granular data.
Setting Up Automated Indexing Alerts
GSC sends email notifications when it detects significant indexing errors, but these alerts are often delayed by days or weeks. By the time you get notified, the problem has already impacted your traffic.
Use GSC's API to pull index coverage data daily. Compare indexed page counts against your publication schedule. If you published 20 posts this week but indexed pages only increased by 2, investigate immediately.
Why AI Content Specifically Faces Indexing Challenges
AI-generated content isn't inherently blocked by Google, but it does face unique indexing hurdles.
Content Quality Signals and Spam Filters
Google's March 2024 Core Update targeted low-value AI content at scale. Sites that relied heavily on unedited AI output saw indexing ratios drop from 80% to under 20%.
According to Originality AI's analysis, "the vast majority of sites which received a manual action were likely using AI content."
Google doesn't penalize AI content because it's AI. It penalizes content that fails to meet quality standards, and unedited AI content often exhibits patterns Google associates with spam:
Generic phrasing with no original perspective
Lack of first-hand data or examples
Repetitive sentence structures
Missing author expertise signals
E-E-A-T Requirements for AI Content
Google's Quality Rater Guidelines emphasize Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. AI content often struggles with the "Experience" component.
If your blog post about "how to choose a CRM" reads like a generic summary of publicly available information, Google has no reason to index it. There are already 10,000 similar pages.
Add original data. Include screenshots from your actual CRM setup. Reference specific workflows your team uses. Those signals tell Google this isn't just regurgitated information.
Duplicate Content at Scale
Many AI content tools pull from the same training data and produce similar outputs for identical prompts. If 50 sites publish AI-generated articles about "best project management software" in the same week, Google sees significant overlap.
Even if each article is technically unique at the word level, semantic similarity can trigger duplicate content filters. Google might index one or two versions and ignore the rest.
Technical SEO Issues Amplified by AI Workflows
AI content automation often bypasses standard editorial checks. This leads to technical issues that slow indexing:
Missing or duplicate title tags
Auto-generated meta descriptions that exceed character limits
Internal linking structures that create orphan pages
Image optimization skipped entirely
These problems exist in human-written content too, but AI workflows publish at such volume that small issues compound quickly.
Getting Started with Keytomic's Auto-Indexing Dashboard
Keytomic handles the entire indexing workflow from keyword research through Google submission, with built-in monitoring to catch failures before they impact traffic.
Connecting Your GSC Property
When you create a new project in Keytomic, you'll connect your Google Search Console property during setup. The platform uses OAuth to authenticate, so you never share passwords.
Once connected, Keytomic pulls your existing index coverage data and baselines your current indexing rate. This lets you track improvement as you publish new content.
Configuring IndexNow Integration
Navigate to Settings → Indexing in your Keytomic project. Enter your IndexNow API key and verify the key file is hosted correctly at your domain root.
Keytomic automatically submits URLs to IndexNow within minutes of publishing. You can view submission logs in the Indexing tab, including timestamps, status codes, and any error messages.
If a submission fails with a 403 error, Keytomic flags it and provides troubleshooting steps: verify key file location, check file encoding, confirm the key matches what's in your settings.
Monitoring Submission Status in Real Time
The Indexing dashboard shows a live feed of all URL submissions: pending, accepted, or failed. Filter by status to quickly identify problematic patterns.
If you're seeing consistent "Crawled — currently not indexed" errors for a specific content type, that signals a quality issue, not a technical problem. You'll need to adjust your content brief or add more original data.
Automated Rollback for Failed Submissions
When Keytomic detects a submission failure due to server errors or temporary GSC outages, it automatically retries the submission after a delay. You can configure retry intervals and max attempts in Settings.
For persistent failures, Keytomic sends Slack or email alerts with diagnostic details. You'll know immediately if your IndexNow key expired or if GSC permissions changed.
Index Coverage Analytics
Keytomic's Analytics tab compares your index coverage against publication volume. You'll see charts showing:
URLs published per week
URLs indexed per week
Average time-to-index
Error rate by category
If time-to-index suddenly spikes from 3 days to 14 days, that's an early warning signal. Check for recent site changes, server performance issues, or content quality drops.
Troubleshooting Persistent Indexing Failures
You've verified permissions, fixed your IndexNow setup, and submitted URLs correctly. But pages still aren't indexing. Here's what to check next.
Review Content Quality Benchmarks
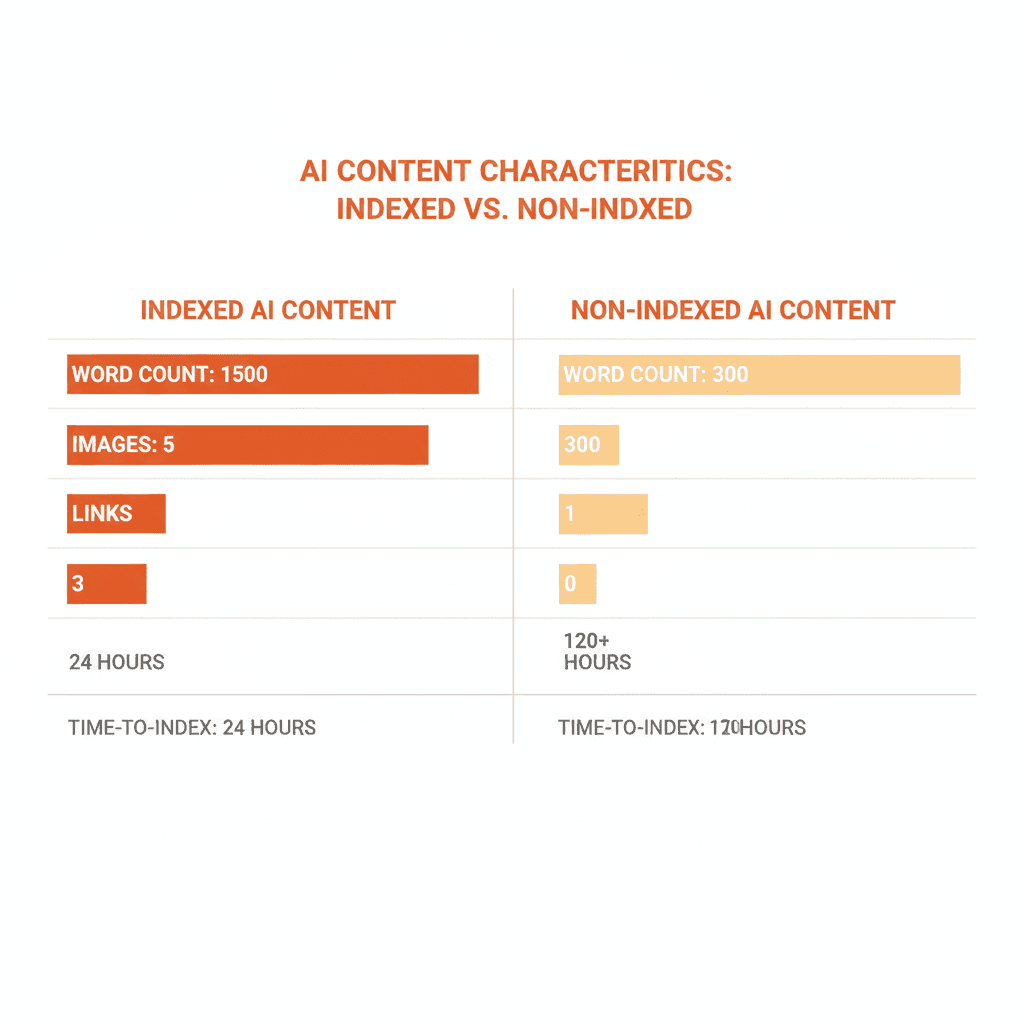
Compare your non-indexed AI content against pages that did get indexed. Look for differences in:
Word count and depth
Use of original data or examples
Internal and external linking patterns
Image inclusion and optimization
Author bylines and credentials
If indexed pages average 1,800 words with 5 screenshots and non-indexed pages are 600 words with no images, that tells you where to adjust.
Check Server Response Times
Use Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to measure page load speeds. If your AI content pages take 8+ seconds to load, Googlebot might time out during crawling.
Optimize images, enable caching, and consider a CDN. Faster load times improve crawl efficiency and indexing success rates.
Verify JavaScript Rendering
If your site relies on JavaScript to render content, Google's crawler might not see the full page. Use the URL Inspection Tool's "View rendered HTML" option to see what Googlebot actually sees.
If critical content appears in the browser but not in rendered HTML, you have a JavaScript rendering problem. Solutions include server-side rendering or prerendering tools.
Audit Internal Linking Structure
Orphan pages with no internal links from other pages on your site are hard for Google to discover and less likely to be indexed. Check that every new AI-generated post is linked from:
Your blog archive or category pages
Related posts sections on similar articles
Navigation menus or footer links where relevant
Keytomic's internal linking recommendations help identify orphan pages and suggest linking opportunities based on topical relevance.
Monitor Crawl Budget Allocation
Large sites with limited crawl budget might not get all pages crawled frequently. Check your GSC Crawl Stats report to see how many pages Googlebot crawls per day.
If crawl rate is dropping while you're publishing more content, you might be hitting crawl budget limits. Prioritize high-value pages in your sitemap and use robots.txt to block low-value sections like filters or search result pages.
Why Agencies Choose Keytomic for Multi-Client Auto-Indexing
Managing indexing workflows for 20+ client sites manually is impossible. Keytomic centralizes monitoring and automates the tedious parts.
Centralized Indexing Dashboard for All Clients
View indexing status across all client projects in one dashboard. Filter by client, time range, or error type to quickly spot issues.
If five clients suddenly show increased "Server error" responses, you know there's a hosting provider issue, not a client-specific problem.
White-Label Reporting
Generate client reports showing indexed pages, submission success rates, and time-to-index metrics. Add your agency branding and export as PDF.
Clients see the value of your SEO automation work without needing to understand the technical details of GSC error codes.
Automatic Error Escalation
Set custom alert thresholds per client. If a client's indexing rate drops below 50%, Keytomic sends an alert to your team Slack channel with diagnostic details.
You can resolve issues before clients notice traffic drops.
API Access for Custom Integrations
Keytomic's API lets you build custom workflows. Trigger indexing submissions from your CMS publish hook, integrate with project management tools, or feed indexing data into your analytics warehouse.
Agencies with unique workflows can automate beyond what's available in the UI.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take Google to index submitted URLs?
Typically 3-7 days for new content, faster for updates to existing pages. High-authority sites often see indexing within 24 hours.
Does submitting via IndexNow guarantee indexing?
No. IndexNow notifies search engines of changes but doesn't override quality filters. Content must still meet Google's standards.
Can I fix "Crawled — currently not indexed" errors?
Improve content depth, add original data, strengthen internal linking, and ensure pages meet E-E-A-T standards. Resubmit after improvements.
Why do some pages index immediately while others take weeks?
Google prioritizes pages based on site authority, content freshness, and perceived value. New sites or low-authority pages index slower.
What's the difference between GSC URL submission and IndexNow?
GSC submission targets Google only. IndexNow notifies multiple search engines (Bing, Yandex, etc.) simultaneously with one API call.






